Black-bellied Plover
General Description
The Black-bellied Plover is Washington's largest plover. The breeding adult male is solid black from chin to belly. The upperparts are white or white mottled with black. The female is more brownish than black. Juveniles and birds in non-breeding plumage are speckled gray-brown above with a gray-brown breast and white belly. A white rump is visible in all plumages. The breast and sides are heavily streaked in the juvenile. In flight, black axillaries contrast with white under-wing coverts.
Habitat
Black-bellied Plovers winter on sandy beaches and estuarine mud flats around the world. They are also found in wet, plowed fields and grassy meadows near the coast and on inland marine waters. They nest on dry arctic tundra.
Behavior
Black-bellied Plovers often roost and fly in flocks, but spread out when foraging. In winter, they commonly feed in association with Dunlin. Like other plovers, Black-bellied plovers are visual feeders, but they may also probe for hidden prey.
Diet
On their wintering grounds, Black-bellied Plovers feed on polychaete worms, bivalves, and crustaceans. On their breeding grounds, they primarily eat insects.
Nesting
The Black-bellied Plover nests on dry tundra, often on a raised area with good visibility. The male begins a scrape nest, and the female lines it with pebbles and bits of vegetation. Females typically lay four eggs, and both parents incubate. The young may forage within 12 hours, but tend to stay in the nest longer than other shorebirds. Both parents care for the young and have one brood per season.
Migration Status
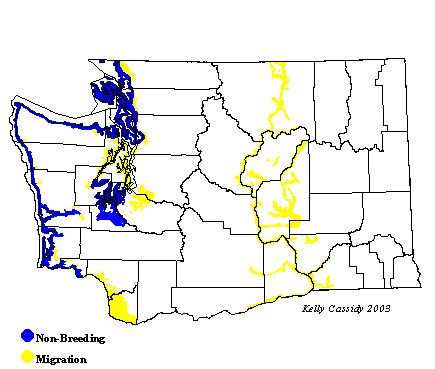
Although Black-bellied Plovers occur year round on the outer coast of Washington, they are especially common during migration (April to May and July to October) and in winter. Immatures of both sexes can be seen throughout the summer.
Conservation Status
Their arctic breeding habitat is at low risk of human occupation and development. Christmas Bird Counts indicate that regional wintering populations are increasing.
When and Where to Find in Washington
Black-bellied Plovers can be found year round on outer beaches such as Ocean
Shores, Grays Harbor, and Leadbetter Point, but are less common in the summer, when only non-breeders remain. They are uncommon in Puget Sound. Juveniles regularly migrate through the interior, especially from late August to October.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | C | C | C | C | C | R | U | C | C | C | C | C |
| Puget Trough | F | F | F | F | U | R | R | C | C | F | F | F |
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | ||||||||||||
| East Cascades | ||||||||||||
| Okanogan | R | R | ||||||||||
| Canadian Rockies | ||||||||||||
| Blue Mountains | ||||||||||||
| Columbia Plateau | R | R | U | U |
Washington Range Map
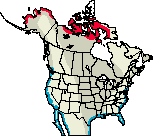
North American Range Map

Family Members
 Black-bellied PloverPluvialis squatarola
Black-bellied PloverPluvialis squatarola American Golden-PloverPluvialis dominica
American Golden-PloverPluvialis dominica Pacific Golden-PloverPluvialis fulva
Pacific Golden-PloverPluvialis fulva Snowy PloverCharadrius alexandrinus
Snowy PloverCharadrius alexandrinus Semipalmated PloverCharadrius semipalmatus
Semipalmated PloverCharadrius semipalmatus Piping PloverCharadrius melodus
Piping PloverCharadrius melodus KilldeerCharadrius vociferus
KilldeerCharadrius vociferus Mountain PloverCharadrius montanus
Mountain PloverCharadrius montanus Eurasian DotterelCharadrius morinellus
Eurasian DotterelCharadrius morinellus

